Here, we can prove and learn differentiation formulas like the product rule, power rule, Quotient rule, trigonometric function derivative, constant derivative and much more. All proofs are available below.
Derivative of product rule or differentiation of product rule
let ![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are function of
are function of ![]()
![]()
![]()
Derivative of quotient rule or differentiation of quotient rule
![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are function of
are function of ![]()
![]()
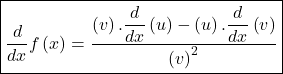
Derivative of power rule or differentiation of power rule
![]()
![]()
![]()
Derivative of chain rule or differentiation of chain rule
Let ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
Derivative of trigonometric functions or Differentiation of trigonometric functions
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Derivative of inverse trigonometric functions ,Differentiation of inverse trigonometric functions
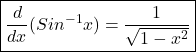
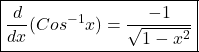
![]()
![]()
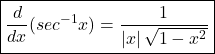
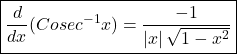
Derivative of sum and difference rule, Differentiation of sum and difference rule
sum rule of Derivative
let ![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are function of
are function of ![]()
![]()
difference rule of Derivative
let ![]()
where ![]() and
and ![]() are function of
are function of ![]()
![]()
Derivative of hyperbolic functions
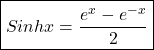
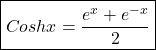
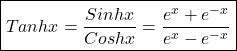
![]()
![]()
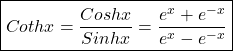
Logarithmic differentiation
![]()
Derivative of constant is zero
![]()
