Field definition math: A set S is called a field if the operations of addition ‘+ ’ and multiplication ‘. ’ on S satisfy
the following properties are written in tabular form:
| Addition |
| Closure for any set Commutativity for any Associativity for any Existence of Identity for any such that Existence of Inverses for any such that Distributivity for any 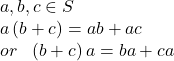 |
| Multiplication |
| closure for any set Commutativity for any Associativity for any Existence of Identity for any such that Existence of Inverses for any such that Distributivity for any 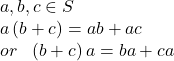 |
All the above mentioned properties hold for ![]() .
.
Hence ![]() are a field in math
are a field in math
